The XDAS Architecture
The Audit Record Framework implements the OpenGroup XDAS specification. XDAS provides several key features to instrumented applications: One of these features is the common audit record format. Another key feature is a standardized audit event taxonomy that allows audit records to be classified in a well-known manner. Well-known classification is one of the power points of ARF, since it allows interoperability among tools. The diagram below illustrates the software components of XDAS.
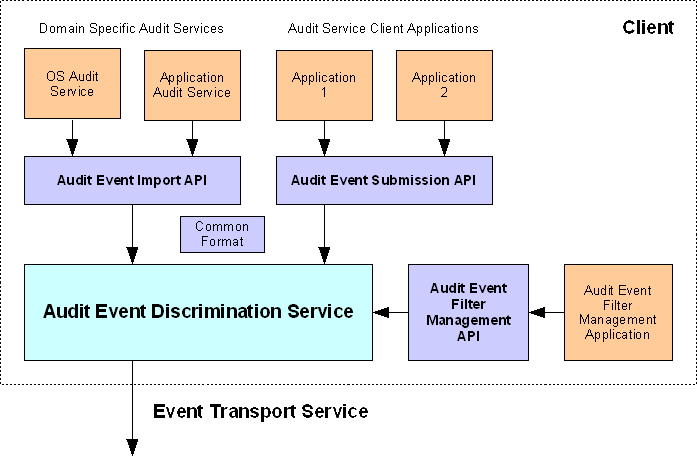
This diagram shows three colors. The light orange color indicates applications - basically clients of the XDAS library.
The OpenXDAS library contains several APIs, shown in purple in the diagram above. The submission API is the most notable, as this API is used by instrumented applications to submit audit records to the auditing system. Another important API is the filter management API, which allows audit system management applications to specify which events get transmitted, and which are simply dicarded as unimportant. The import API allows an import service to convert domain-specific audit records such as Windows WMI audit records or Unix Syslog audit records into the common XDAS format, and the pass them on to the XDAS data store. These API's make up the client-side audit instrumentation and management library.
The light green box, indicates the client-side event discrimination service. This is a daemon service running on each audit-enabled host, which manages the client-side filtering criteria - a database of filters specified via configuration and the filter management API. This service listens for audit events from each instrumented application, and forwards those events that are not filtered out to a (possibly remote) XDAS audit server.
Data Model
The standardized event types specified by XDAS are simple, but comprehensive:
- XDAS_AE_CREATE_ACCOUNT - Create account
- XDAS_AE_DELETE_ACCOUNT - Delete account
- XDAS_AE_DISABLE_ACCOUNT - Disable account
- XDAS_AE_ENABLE_ACCOUNT - Enable account
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_ACCOUNT - Query account attributes
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_ACCOUNT - Modify account attributes
- XDAS_AE_CREATE_SESSION - Create a user session
- XDAS_AE_TERMINATE_SESSION - Terminate a user session
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_SESSION - Query a user session attributes
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_SESSION - Modify user session attributes
- XDAS_AE_CREATE_DATA_ITEM - Create data item
- XDAS_AE_DELETE_DATA_ITEM - Delete data item
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_DATA_ITEM_ATT - Query data item attributes
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_DATA_ITEM_ATT - Modify data item attributes
- XDAS_AE_INSTALL_SERVICE - Install service or application
- XDAS_AE_REMOVE_SERVICE - Remove service or application
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_SERVICE_CONFIG - Query configuration of service or application
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_SERVICE_CONFIG - Modify configuration of service or application
- XDAS_AE_DISABLE_SERVICE - Disable service or application
- XDAS_AE_ENABLE_SERVICE - Enable service or application
- XDAS_AE_INVOKE_SERVICE - Invoke service or application
- XDAS_AE_TERMINATE_SERVICE - Terminate service or application
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_PROCESS_CONTEXT - Query processing context
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_PROCESS_CONTEXT - Modify processing context
- XDAS_AE_CREATE_PEER_ASSOC - Create an association with a peer
- XDAS_AE_TERMINATE_PEER_ASSOC - Terminate an association with a peer
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_ASSOC_CONTEXT - Query an association context
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_ASSOC_CONTEXT - Modify an association context
- XDAS_AE_RECEIVE_DATA_VIA_ASSOC - Receive data via an association
- XDAS_AE_SEND_DATA_VIA_ASSOC - Send data via an association
- XDAS_AE_CREATE_DATA_ITEM_ASSOC - Create association with data item
- XDAS_AE_TERMINATE_DATA_ITEM_ASSOC - Terminate association with data item
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_DATA_ITEM_ASSOC_CONTEXT - Query context of association with data item
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_DATA_ITEM_ASSOC_CONTEXT - Modify context of association with data item
- XDAS_AE_QUERY_DATA_ITEM_CONTENTS - Query data item contents
- XDAS_AE_MODIFY_DATA_ITEM_CONTENTS - Modify data item contents
- XDAS_AE_START_SYS - Start system
- XDAS_AE_SHUTDOWN_SYS - Shutdown system
- XDAS_AE_RESOURCE_EXHAUST - Resource exhaustion
- XDAS_AE_RESOURCE_CORRUPT - Resource corruption
- XDAS_AE_BACKUP_DATASTORE - Backup datastore
- XDAS_AE_RECOVER_DATASTORE - Recover datastore
- XDAS_AE_AUD_CONFIG - Configure audit service
- XDAS_AE_AUD_DS_FULL - Audit datastore full
- XDAS_AE_AUD_DS_CORR - Audit datastore corrupted
These events are arranged into a two-level hierarchy, the top level of which specifies the class of event type, while the leaf level is the actual event type.
Account Management Events
This set of events is applicable to the management of principal accounts. A principal may be an end-user or a service within the system, a psuedo-user.
- Create account - the creation of an account representing a principal within a domain.
- Delete account - the deletion of an account representing a principal from a domain.
- Disable account - an action the prevents a principal account from being used within a domain.
- Enable account - an action that permits a principal account to be used within a domain.
- Query account attributes - the requesting of the attributes associated with a principal within a domain.
- Modify account attributes - the modification of the attributes associated with a principal within a domain.
User Session Events
This set of events is relevant to the creation and use of user sessions on the system.
- Create a user session - the establishment of a processing environment to service an end user.
- Terminate a user session - the dismantling of a processing environment associated with servicing an end user.
- Query user session attributes - the requesting of the attributes associated with a user session.
- Modify user session attributes - the modification of security significant attributes of the context of a processing environment servicing an end user.
Data item and Resource Element Management Events
This set of events relate to the creation and management of data items and resource elements within a domain. The type of data item or resource element is dependent upon the domain, e.g., files and directories, device special files, shared memory segments, within an operating system, tables and records within a database, messages within an email system. The term data item is used to refer to any type of resource element.
- Create data item - creation of a data item within a domain.
- Delete data item - deletion of a data item from a domain.
- Query data item attributes - the requesting of the attributes associated with a domain data item.
- Modify data item attributes - the modification of the security attributes of a domain data item such as access control attributes, ownership, aliases.
Service or Application Management Events
This set of events relate to the management of system services and applications.
- Install service or application - the installation of additional or updated software on a system, e.g., an application or system service.
- Remove service or application - the deinstallation of software on a system.
- Configure service or application - the modification of the configuration data associated with a software component.
- Query configuration of service or application - the requesting of information about the configuration of a service or application.
- Disable service or application - an action that prevents an application or system service from being used, for example, inhibiting responses to service requests. It may also involve the termination (shutdown) of application processing components that are currently providing the service.
- Enable service or application - an action that permits an application or system service to be used, for example, allowing responses to service requests. This may also involve the invocation of specific application processing components (startup).
Service and Application Utilization Events
These events relate to the use of service and applications. They typically map to the execution of a program or a procedure and manipulation of the processing environment.
- Invoke service or application - the invocation of a service or application (exec), e.g., operating system utility, database, accounting application, etc.
- Terminate service or application component - the termination (exit) of the use of a service or application. This could be at the instigation of the application itself or by the intervention of the domain in response to user or administrative action.
- Query processing context - the requesting of the attributes associated with the current processing environment.
- Modify processing context - the modification of the attributes associated with the current processing environment.
Peer Association Management Events
- Create an association with a peer - the creation of a communication channel and the processing context between system components.
- Terminate an association with a peer - the closure of a communications channel and destruction of processing context between system components.
- Query an association context - the requesting of the attributes of a context associated with a communications channel between peers.
- Modify an association context - the modification of the attributes of a processing context associated with a communications channel.
- Receive data via an association - receiving data from associated peer within current association context.
- Send data via an association - sending data to associated peer within current association context.
Data Item or Resource Element Content Access Events
These events relate to the formation of an association between a service or application and a data item or resource element for the purpose of using its contents or services. For example, a file or directory, device special file, memory segment, communications port, etc.
- Create association with data item - create an association with (open) a data item. This creates a binding between the caller and the data item.
- Terminate association with data item - the termination of an existing association with (close) a data item.
- Query context of association with data item - the requesting of the context of an association with a data item, e.g., mode of access, size limits, access path, etc.
- Modify context of association with a data item - the modification of the context of an association with a data item or resource element.
- Query data item contents - the requesting of the contents of a domain data item (read).
- Modify data item contents - the modification of the contents of a domain data item (write, append, etc.).
Exceptional Events
These are events that are considered to be outside the generalized events listed above.
- Start system - the action of booting a system host or of changing the processing state of a system host to an operational mode.
- Shutdown System - the action of halting the processing by a system host or of changing the processing state of a system host to a maintenance mode.
- Resource exhaustion - the detection of resource exhaustion which has a potential impact on system operations, perhaps based upon a configurable threshold, e.g., data storage resources, communication end points.
- Resource corruption - the detection of an integrity failure of a system resource, for example data storage resource.
- Backup datastore - the action of making a backup copy of a datastore for the purposes of protecting availability and integrity of the data it contains.
- Recover datastore - the action of restoring the contents of a datastore from a previously made backup copy for the purposes of restoring the availability of the contents, or the integrity of the contents, or both.
Audit Service Management Events
These are events of specific relevance to the audit service itself.
- Configure audit service - the modification of the parameters controlling the operation of the audit service, for example, audit event filtering criteria.
- Audit datastore full - the detection of resource exhaustion for the particular instance of the resource used to store the log of audit event records.
- Audit datastore corrupted - the detection of a datastore integrity failure for the particular instance of the resource used to store the log of audit event records.
Audit Events may be specifically referenced by an Event Number. A set of Audit Events may be referred to by an Event Class. The concept of an Event Class is included in the XDAS solely as an administrative convenience. It provides an efficient and convenient reference to sets of audit events so that audit filters can be easily defined. An audit event record only includes the Event Number. It does not include any reference to Event Class for two reasons: its inclusion leads to redundant information in the audit record; and the mapping of event classes across administrative domains is problematic. When specified in filtering selection criteria, an event class is translated internally into the individual event numbers.
Default Event Classes
The XDAS defines a default set of event classes. Others can be defined by the implementation and configured by a system administrator to group together XDAS event numbers in a meaningful way. The default set of event classes defined by the XDAS are listed below:
- Account management events
- User session events
- Data item and resource element management events
- Service and application management events
- Peer association management
- Data item or resource element content access events
- Exceptional events
- Audit service management events
The default mapping of events to these event classes is as listed in Section 4.4.2.
Application Programmer's Interface
Full details on the OpenXDAS API can be found on the OpenXDAS website under the documentation link. The API is documented using Doxygen comments, the latest of which can be accessed from the link on the right side of the page.
Configuration
OpenXDAS is configured for remote XDAS audit server and local host persistant filters via a configuration file stored in the /etc/xdas directory - xdas.conf. This file is read by the daemon on startup for filter configuration information, and other configuration data. Configuration options will be added over time, and changes to this page will be made as appropriate.
Event Transport Service
The XDAS standard does not specify the details of the event transport service, leaving it up to individual implementations to determine the best transport service for its requirements. OpenXDAS uses the syslog transport (IETF RFC 3195) mapped onto TLS (currently an IETF draft standard).
RFC 3195 - Reliable Delivery for syslog defines a wire protocol whose XML schema is defined in a DTD. This protocol uses XML over BEEP, which is a highly configurable and open standard for data stream transport. One problem with this approach is that, while the payload of the BEEP message is very unstructured, it's also generally and practically limited to legacy sysload messages - an unstructured string with no embedded CRLF's, and a length that is generally limited to about 1K of data. Bandit ARF will attempt to conform to this wire format to the degree that we can, allowing many existing back-end syslog services to be used as a data store for the Bandit ARF event stream. Where this model breaks down is in the lack of robustness of some syslog servers. Bandit will work with the community to enhance the syslog protocol going forward. If we can't find a syslog server that meets our open source community needs, we'll implement an extended server as part of the Bandit project.
Note: While there are perhaps better wire protocols currently defined for event data, syslog is extremely pervasive, making it an ideal choice for Bandit ARF and OpenXDAS.